Understanding Linear Regression
Linear regression is a key statistical method used in data science to model the relationship between variables. It helps predict the value of a dependent variable based on one or more independent variables.
Concepts of Linear Regression
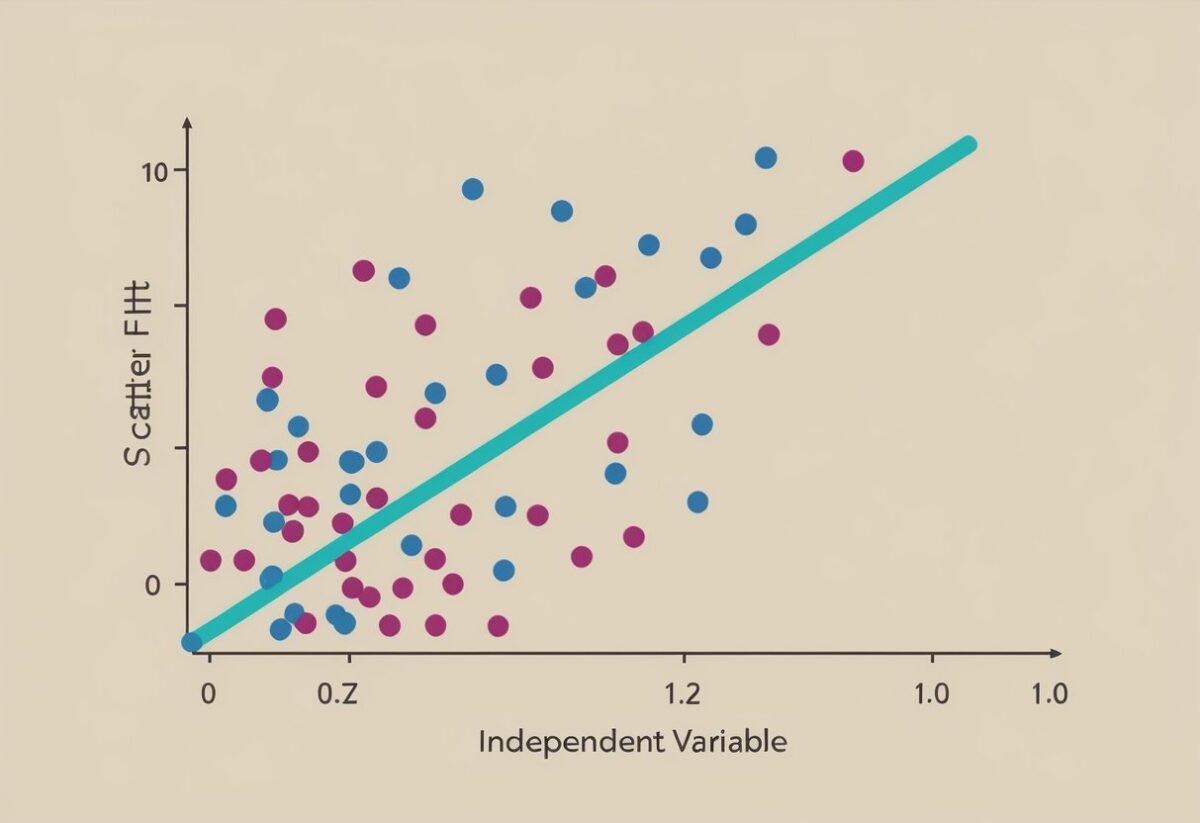
Linear regression focuses on establishing a linear relationship between variables. The regression model is expressed as an equation where the dependent variable, often called the response variable, is predicted from independent variables or predictor variables.
The result is a straight line that best fits the data points, known as the line of best fit.
This method is widely used because of its simplicity and efficiency. The slope of the line indicates the strength and direction of the relationship between the variables. Researchers use this information to make data-driven decisions, like estimating trends over time or understanding how changes in predictors influence the response.
Assumptions of Linear Regression
Linear regression comes with several assumptions that must be satisfied for the model to provide valid results.
Linearity assumes a straight-line relationship between predictor and response variables. This can be verified through scatter plots or residual plots.
Another assumption is independence, which means observations are not related to each other, ensuring accuracy in predictions.
Homoscedasticity is another important assumption, meaning that the variance of residuals is consistent across all levels of the independent variables. Lastly, the normality of residuals suggests that they should approximately follow a normal distribution.
These assumptions are critical to verify when using linear regression to avoid misleading conclusions.
Diving into Residuals
Residuals play a crucial role in understanding linear regression models. They help reveal how well a model fits the data and highlight any potential issues affecting accuracy. This section explores the definition of residuals and their significance in regression analysis.
Defining Residuals
Residuals are the differences between observed values and predicted values generated by a regression model. When a regression line is drawn through data points, it represents the best-fitted values for that dataset. However, not all data points will lie perfectly on this line.
Residuals are these vertical distances: calculated by subtracting the predicted value from the observed value for each data point.
Residuals provide insight into the level of error in a model. A smaller residual indicates that a predicted value closely matches the observed value, while larger residuals suggest greater inaccuracies.
Residuals can help identify outliers, points that significantly deviate from the expected pattern of the regression line. Such deviations could indicate that other variables might influence the data or that the model needs adjustment.
The Role of Residuals in Regression
Residuals are vital in evaluating the effectiveness of a regression model. They are used in residual analysis, which examines the distribution and pattern of these errors.
A good model will have residuals that are randomly distributed with no discernible pattern. If the residuals display a pattern, it can suggest issues like non-linearity, heteroscedasticity, or model misspecification.
Residual plots, graphical representations of residuals, help assess these aspects visually.
For example, patterns such as a funnel shape in a residual plot may indicate heteroscedasticity, where the variance of errors differs across observations. Consistent residuals can highlight a need for using different techniques or transformations to improve model fit.
Residual analysis aids in enhancing model accuracy and ensuring the reliability of conclusions drawn from regression.
Exploring Residual Plots
Residual plots are essential tools in analyzing linear regression models. They offer valuable insights into the suitability of the model by showing how residual values are distributed and if any patterns exist.
Purpose of Residual Plots
Residual plots serve as a graphical representation of the differences between observed and predicted values in regression models. By plotting residual values against the predicted values or independent variables, one can assess the adequacy of a linear regression model.
Using these plots, one can detect non-linearity, identify heteroscedasticity, and pinpoint influential data points that might affect the model’s accuracy. A plot with a random pattern suggests that the model is appropriate, while visible patterns indicate potential issues.
Interpreting Residual Plots
When interpreting a residual plot, several factors are taken into account. A scatter plot of residuals should appear randomly distributed with no clear patterns for a well-fitting model.
Patterns like a funnel shape could suggest heteroscedasticity, where the variance of errors changes across levels of independent variables.
Symmetry around the horizontal axis is a desirable property. It implies that errors are evenly distributed, confirming the model’s assumptions. Observing clustering or systematic trends might suggest model inadequacies or that important predictor variables are missing.
Checking for these aspects enhances residual plot analysis and ensures the model’s reliability in predicting outcomes.
For more insights on how these characteristics are crucial in regression models, you can explore resources like this comprehensive guide.
Elements of a Residual Plot
Residual plots are essential for assessing linear regression models. They help identify patterns and outliers that might indicate issues with the model. Recognizing these elements is crucial to ensure model accuracy.
Detecting Patterns in Residual Plots
A residual plot shows the residuals on the y-axis and the fitted values on the x-axis. An ideal residual plot displays a random pattern. This randomness suggests that the model is capturing all systematic information, and errors are randomly distributed.
Patterns to watch for:
- Linear patterns: May suggest that a linear relationship is not suitable.
- U-shaped patterns: Can indicate issues like missing variables or incorrect model form.
- High density of points close to the zero line typically indicates a good model fit. Consistency across the horizontal line without forming a clear pattern is key.
A random scatter around the horizontal axis is one of the main characteristics of a good residual plot.
Identifying Outliers and Leverage Points
Outliers appear as points that do not follow the trend of the other points. These points can influence the regression line and skew results.
- Outliers: They can distort the model’s predictions and need careful consideration. Identifying them requires looking for points far from the zero line.
- Leverage points: Unlike typical outliers, these are influential points with high leverage, usually located far from the mass of other data points in terms of x-values. They have the potential to greatly affect the slope of the regression line.
Addressing outliers and leverage points ensures a more reliable model, as these points can lead to biased conclusions if not handled properly.
Statistical Software Tools
Python offers powerful tools for statistical analysis and visualization. Libraries such as Seaborn and Statsmodels stand out by providing robust capabilities for linear regression and residual plot analysis.
Introduction to Python Libraries
Python is widely used in data science due to its extensive collection of libraries for statistical analysis.
Numpy is foundational, offering support for arrays and matrices and many mathematical functions. This support is crucial for handling data sets efficiently.
Another essential library is Matplotlib, which works seamlessly with Numpy for plotting graphs. This makes it easier to visualize complex data relationships and trends.
By leveraging these libraries, users can perform linear regression analysis and create residual plots that illuminate the performance of their data models without diving into overly complex computations.
Utilizing Seaborn and Statsmodels
Seaborn is built on top of Matplotlib, providing a high-level interface for drawing attractive and informative statistical graphics. It simplifies the process of creating residual plots and enhances the visual appeal of data visualizations.
On the other hand, Statsmodels offers a plethora of classes and functions to explore data and estimate statistical models. It also provides built-in functionality for regression analysis, making it easy to assess model assumptions via residual plots.
Using Seaborn and Statsmodels together allows users to effectively analyze and present their regression results, making insights more accessible to non-technical audiences. The combination of these tools offers a comprehensive environment for statistical modeling in Python.
Assessing Model Fit
Assessing model fit is crucial in confirming if a regression model accurately represents the relationship in the data. It involves examining the pattern of residuals and computing specific statistical metrics to ensure precision and reliability.
Analyzing the Residual Distribution
Residuals are the differences between observed and predicted values. A well-fitted model shows a random pattern of residuals scattered around the horizontal axis. If residuals have a funnel shape or curve, this could suggest a poor fit.
Residual plots and scatter plots help visualize these patterns.
Standardized residuals give a clearer picture by adjusting residuals based on their variance. A normal distribution of standardized residuals indicates good model performance.
Correlation and Determination Metrics
R-squared is a key metric in evaluating a regression model. It measures the proportion of variability in the dependent variable explained by the independent variables. A higher R-squared value indicates a better fit, although it does not guarantee prediction accuracy.
MAPE (Mean Absolute Percentage Error) is another important metric. It measures prediction accuracy by calculating the percentage difference between observed and predicted values. This helps in understanding the model’s performance. Reliable models have lower MAPE values.
Distribution of Residuals
In linear regression, checking the distribution of residuals is essential. It helps ensure that the assumptions of the model are met, leading to reliable results. This involves examining normality and testing for homoscedasticity.
Normality in Residuals
Residuals should ideally follow a normal distribution. When residuals are plotted, they should form a symmetric pattern centered around zero.
A normal Q-Q plot provides a graphical method to assess normality.
In this plot, the residual quantiles are compared to the quantiles of a normal distribution. Points lying on or near the line indicate normal residuals. Deviations might suggest that the data does not meet the assumptions of the linear regression, which can affect predictions.
Identifying non-normality allows for adjustments or transformations to improve the model fit.
Testing for Homoscedasticity
Homoscedasticity refers to the residuals having constant variance across different levels of the predictor variables. This means the spread of residuals remains stable, an assumption of linear regression models.
A disturbance in this variance, known as heteroscedasticity, can distort the model’s credibility.
Visual inspection of a residual plot can reveal variance issues. Ideally, the residuals should display a random spread without any clear pattern.
Consistent variance ensures the accuracy and reliability of the model’s predictions. Detecting heteroscedasticity may require transforming variables or employing weighted regression techniques. These adjustments can lead to a more stable relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Complexities in Linear Models
Understanding the complexities in linear models involves analyzing factors like heteroscedasticity and the independence of error terms. These aspects are crucial for improving the accuracy and reliability of the models.
Heteroscedasticity and its Effects
Heteroscedasticity occurs when the variance of error terms varies across observations.
In a linear regression model, this can lead to inefficient estimates, potentially skewing predictions.
The presence of heteroscedasticity might suggest that the model does not fully capture the data’s complexity.
Identifying heteroscedasticity often involves examining residual plots. A pattern in these plots indicates potential issues.
Correcting heteroscedasticity usually requires transforming the data or using weighted least squares to achieve homoscedasticity, where variances are consistent.
Addressing heteroscedasticity is essential for improving model performance. It helps ensure that predictions are as accurate as possible, allowing the model to generalize well to new data.
Evaluating Independence of Errors
The independence of error terms is another important complexity. It means that the error of one observation should not influence another.
When errors are correlated, it suggests a violation of a key regression assumption, affecting the model’s validity.
Detecting lack of independence can be done using tests like the Durbin-Watson statistic, which helps identify autocorrelation, commonly found in time series data.
Correcting for correlated errors might involve modifying the model structure or using techniques like differencing data points in time series.
Ensuring error independence helps in maintaining the integrity of predictions and enhances the usability of the model.
Advanced Regression Types
Advanced regression models go beyond basic applications, providing deeper insights and more accurate predictions. Two key topics in this area are contrasting multiple linear regression with simple linear regression and understanding their applications in various fields.
Exploring Multiple Linear Regression
Multiple linear regression is a powerful technique that helps in predicting the value of a dependent variable using two or more independent variables.
This model is beneficial in situations where a single predictor isn’t sufficient to explain the variability in the target variable. In the context of machine learning, multiple linear regression is used to uncover relationships in complex data sets.
The process begins with identifying variables that might be relevant, testing their significance, and ensuring the model meets key assumptions like linearity and homoscedasticity.
By evaluating the relationships among multiple variables, this method provides more comprehensive insights compared to simpler models.
Simple vs. Multiple Linear Regression Comparisons
Simple linear regression involves only one independent variable used to predict a dependent variable.
This model is beneficial for understanding the basic influence of a single predictor, but it often lacks the depth required for nuanced analyses. In contrast, multiple linear regression incorporates several predictors, enabling it to address more intricate datasets.
The choice between these methods depends on the research question and the complexity of the data.
When the impact of multiple factors needs to be assessed simultaneously, multiple linear regression becomes essential. Machine learning techniques often prefer multiple predictors for better performance and accuracy in real-world applications.
Case Examples in Regression Analysis
In regression analysis, practical examples from different fields highlight how this statistical method can be applied to understand patterns and make predictions. Applications range from economic forecasting to enhancing sports performance.
Economic Data and Market Trends
Regression analysis plays a key role in analyzing economic data. Economists use it to examine market trends and make predictions about future conditions.
By analyzing historical data, they can identify patterns and factors such as interest rates, unemployment, and inflation. Analysts model these relationships to forecast economic outcomes.
A dataset containing variables like GDP growth and consumer spending can help predict future economic conditions.
This analysis aids in policy-making and business strategy planning. Companies use regression models to predict sales based on various market indicators. These insights enable stakeholders to adjust strategies according to predicted economic shifts effectively.
Sports Performance Analytics
In sports, regression analysis enhances performance evaluation and predictions. For basketball players, statistical models evaluate and predict various performance metrics like scoring, rebounds, and assists.
Data science tools process vast datasets containing game statistics and player attributes. Regression models help teams identify key performance drivers and potential areas of improvement.
For instance, by examining past player performances, teams can predict future player contributions and overall team success.
Using regression, coaches can make informed decisions on player selection and match strategies to optimize performance outcomes. This analytical approach fosters a competitive edge by leveraging data-driven insights into athletic performance.
Practical Applications of Residual Analysis
Residual analysis is vital for enhancing regression models. It’s used in diverse fields to improve predictions and decisions. By examining residuals, professionals can ensure data models accurately reflect real-world dynamics.
Residuals in Business and Finance
In the business and finance sectors, residuals play a crucial role in assessing investment models.
By analyzing residuals, financial analysts can determine the reliability of linear regression models used for forecasting stock prices or market trends. A random distribution of residuals suggests that the model is well-suited to the data, enhancing confidence in financial predictions.
Businesses also use residuals to evaluate customer behavior models. By checking residual patterns, firms can refine marketing strategies and improve customer retention.
For instance, if residuals show patterns, it may indicate that factors influencing sales are not fully accounted for, guiding businesses to adjust their models accordingly.
Healthcare and Residual Plot Utilization
In healthcare, residual plots assist in refining predictive models for patient outcomes.
By analyzing residuals, medical researchers can ensure that the machine learning models used for predicting disease progression are accurate. Patterns in residuals might reveal unaccounted variables such as lifestyle factors in a patient’s health prediction model.
For healthcare management, residual analysis of cost models can identify inefficiencies in hospital operations.
If residuals show a systematic pattern, it might suggest that external factors, like regional healthcare policies, are not fully reflected in the cost predictions. This helps healthcare managers tweak their models for better accuracy and resource allocation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Residual plots are important tools in linear regression analysis, offering insights into model fit and potential problems. They help in determining whether a linear relationship is adequate, what kind of patterns exist, and if the residuals suggest any issues.
How do you interpret a residual plot in linear regression?
In a residual plot, residuals should scatter randomly around the horizontal axis. This pattern suggests a good fit between the model and the data.
If residuals form a pattern, it indicates non-linearity or other issues. A random spread shows that the model’s assumptions hold true.
What indicates a good or bad residual plot?
A good residual plot is one where residuals are evenly distributed around the axis, showing no clear pattern. A bad residual plot shows structured patterns, like curves or clusters, indicating problems like heteroscedasticity or non-linearity.
Can you describe different types of residual plots?
Residual plots can vary. A common type is plotting residuals against predicted values. Another is plotting against each independent variable. Each type helps check different aspects of the model, like variance consistency and linearity. Residual histograms can also show normality of the residual distribution.
How can you identify patterns in residual plots?
Patterns in residual plots, such as curved lines or systematic structures, suggest the model might miss a relationship. Clusters might indicate potential outliers affecting predictions.
These patterns help identify if any assumptions are violated or if transformation of variables is necessary.
What does a residual plot reveal about the fit of a linear model?
Residual plots reveal how well data points fit the linear model by showcasing the residuals’ distribution. Randomly scattered residuals suggest an appropriate fit. Patterns or trends indicate the model might not fit the data well, suggesting a need for revisiting the model.
How do the residuals in linear regression analysis inform model accuracy?
Residuals inform model accuracy by indicating deviations from predicted values.
Smaller and randomly distributed residuals imply higher accuracy and a better model fit.
Large or patterned residuals suggest inaccuracies, indicating the need for further model refinement or alternative approaches.